There are two main reasons why ASE Industries built and tested this reactor. The first was to confirm or invalidate test data that was published in papers regarding hydrothermal biomass conversion. The second reason was to experiment in areas not previously published.  ASE Industries was eager to duplicate a test that was reportedly able to produce methane directly without catalysts at a specific temperature and pressure. The data from the published test also gave a reaction rate for this conversion. Converting biomass to methane without catalysts is highly desirable since catalysts are prone to poisoning (become ineffective) and can be expensive. Our tests, unfortunately, were not able to confirm this test. We suspect that the nickel in the wall of the stainless steel reactor used in the published paper’s test was acting as a catalyst to aid in the speed of the reaction. We were able to convert biomass to methane at these temperatures and pressures without catalysts, but the reaction rate was prohibitively long.
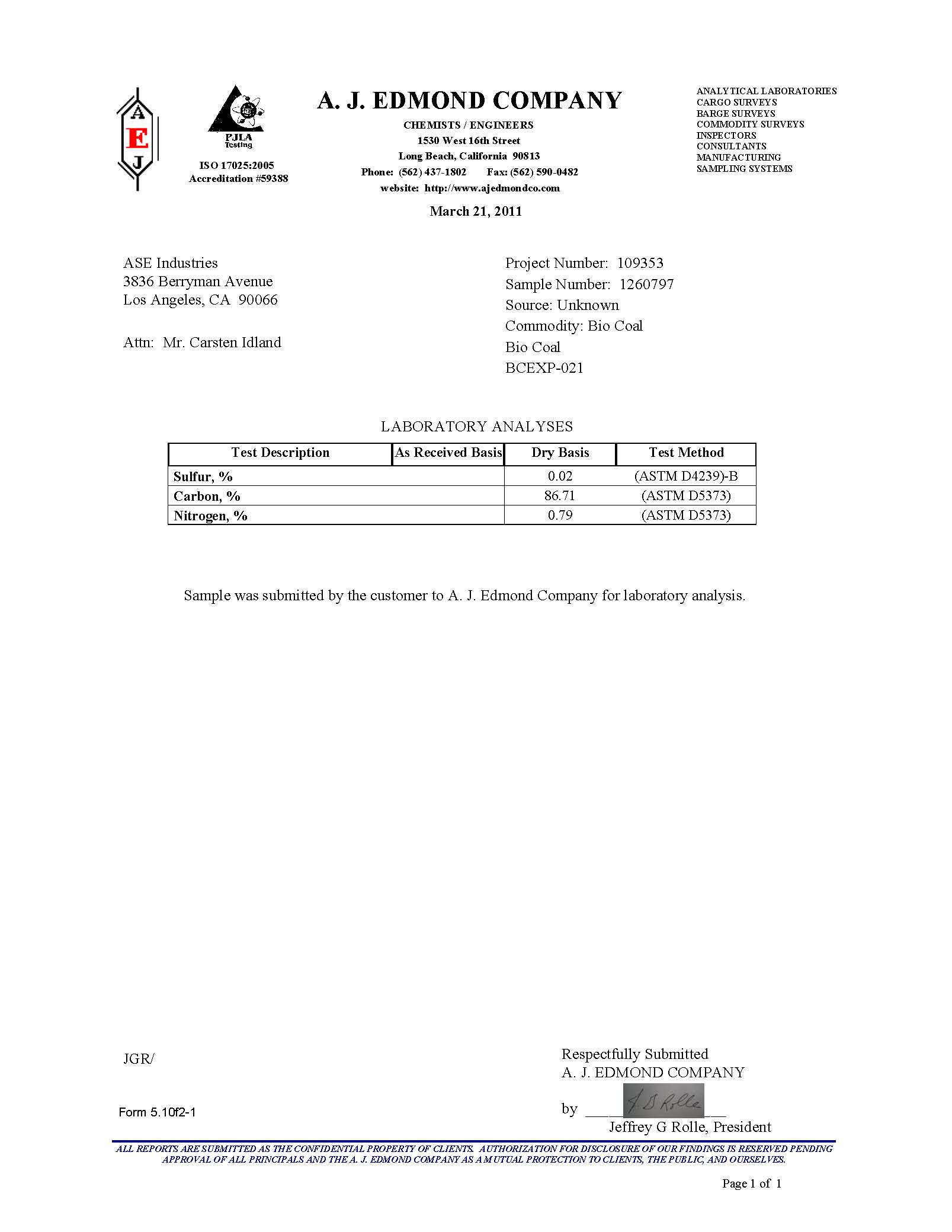
Initially, we had been concentrating in the direct conversion of biomass to methane. We had intended to experiment with catalysts. During our testing we found it quite easy to make biocarbon.  However, this was not our initial goal, so at first we did not put much value in these results. We also found that we could produce methanol fairly easily. We looked into what others were doing in the biomass field, and we found that Canada was selling biocarbon, also known as Biocoal, to Europe. The Europeans were using Biocoal as a carbon offset in their coal plants.  Looking a little further, we found out about the conversion processes for converting coal to gasoline, diesel, and synthetic natural gas. We also found that these processes are currently being implemented in large scale production basis.
It was for these reasons that we further investigated the applications and roles biocarbon could take in the energy portfolio. We are now convinced if implemented the use of biocarbon will play an important and significant role in the world’s energy system.
________________________________________________________________________________
Click on image to enlarge. Click on back page to return.